Blockchain is one of the concepts in the world of technology with more boom in recent years. We see everywhere that big companies are implementing it. It should be something good, but nobody explains to us clearly what it is, what it is for, or why we should use it. Blockchain is for everyone, so this time, I will explain everything I know in a user-friendly format.
Origin
To start, it’s always good to know how it all started. On January 3, 2009, the cryptocurrency called “Bitcoin” came into operation and with it came the new administration paradigm “Blockchain”, in which no kind of bank, government or central entity was needed. At first, it sounds like something insecure, risky, and with a rigged market. However, the reality is blockchain is quite the opposite. Let’s see the details.
Operation
Basically, in Blockchain, intermediaries are removed. Instead, a trusted network is used. The network is made up of participants and regulators, where they help to validate each transaction according to previously established rules. Each transaction is linked to the previous and subsequent ones. Every certain amount of transactions get grouped into blocks. These blocks are also linked and encrypted, using advanced encryption methods. Each user has an identical copy of this registry and the book of rules.
The essential point in Blockchain is that it should have several users, who will be responsible for reviewing, validating and recording each transaction and block. With all these features, we have the basis of a system with great scalability and security. Even millions of users can participate, each transaction and block is validated many times, and the records are extremely difficult to modify. Giving even the possibility of banning users with malicious behavior.
Let’s see a small example
We start a network with 50 users, together according to define these rules:
- All transactions must be validated by at least 10 customers.
- Adding a new customer must be validated by at least 20 customers.
- Everyone must have a record of the transactions.
- The minimum transaction amount is 10 dollars.
“Client1” must pay 50 dollars to “Client 2”, then a transaction is generated, this is sent to 10 active clients for validation, all these clients check if the transaction complies with the rules and “Client 1” has sufficient funds. If everything is ok, then the transaction is accepted and added to the block, then money is moved to “Client 2” finishing the transaction.
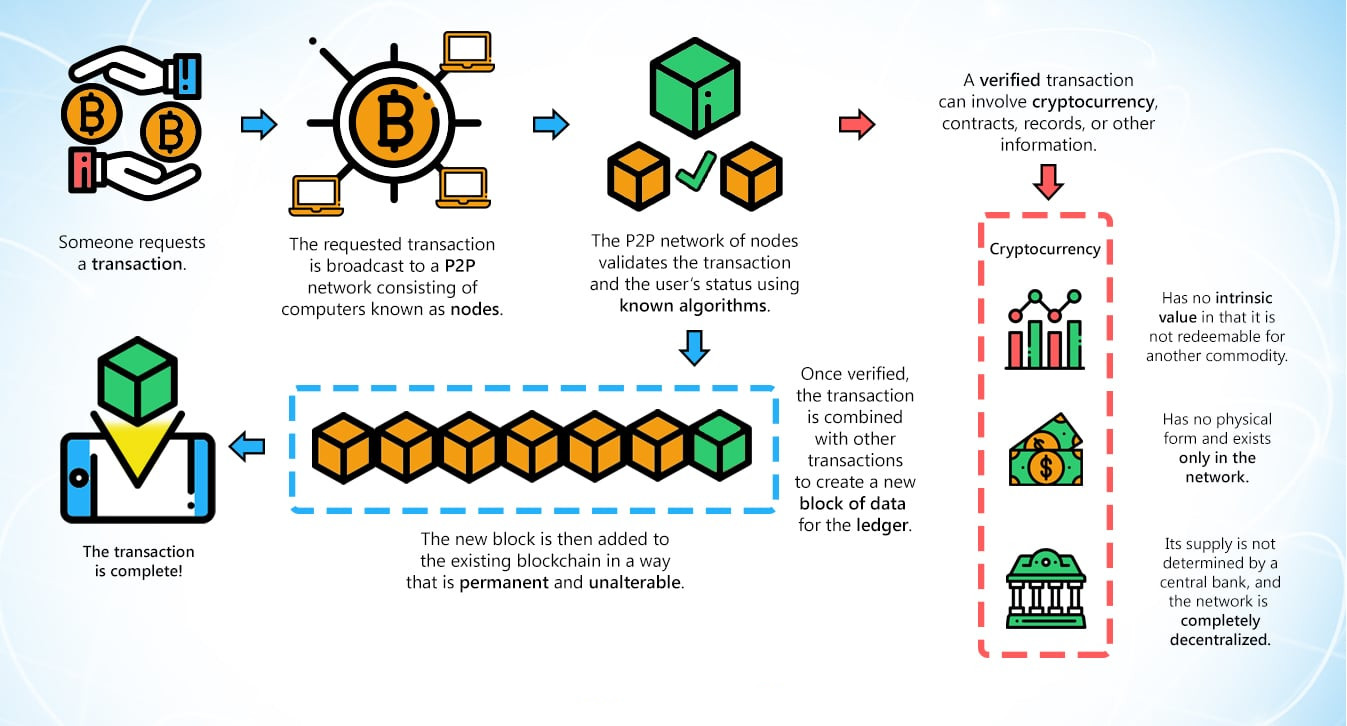
My example is a basic one, but it gives us a better perspective on general Blockchain operations. The process is relatively simple, but this becomes more complicated as nodes and rules are added. As we mentioned before, every transaction is added to a block and after a previously defined number of transactions. When this block is full, it must be validated, encrypted and linked to the chain. This process may require a lot of processing capacity due to the large number of complex calculations needed. There are people who allocate computer resources exclusively for this task in exchange for compensation, this is what is called “Mining”.
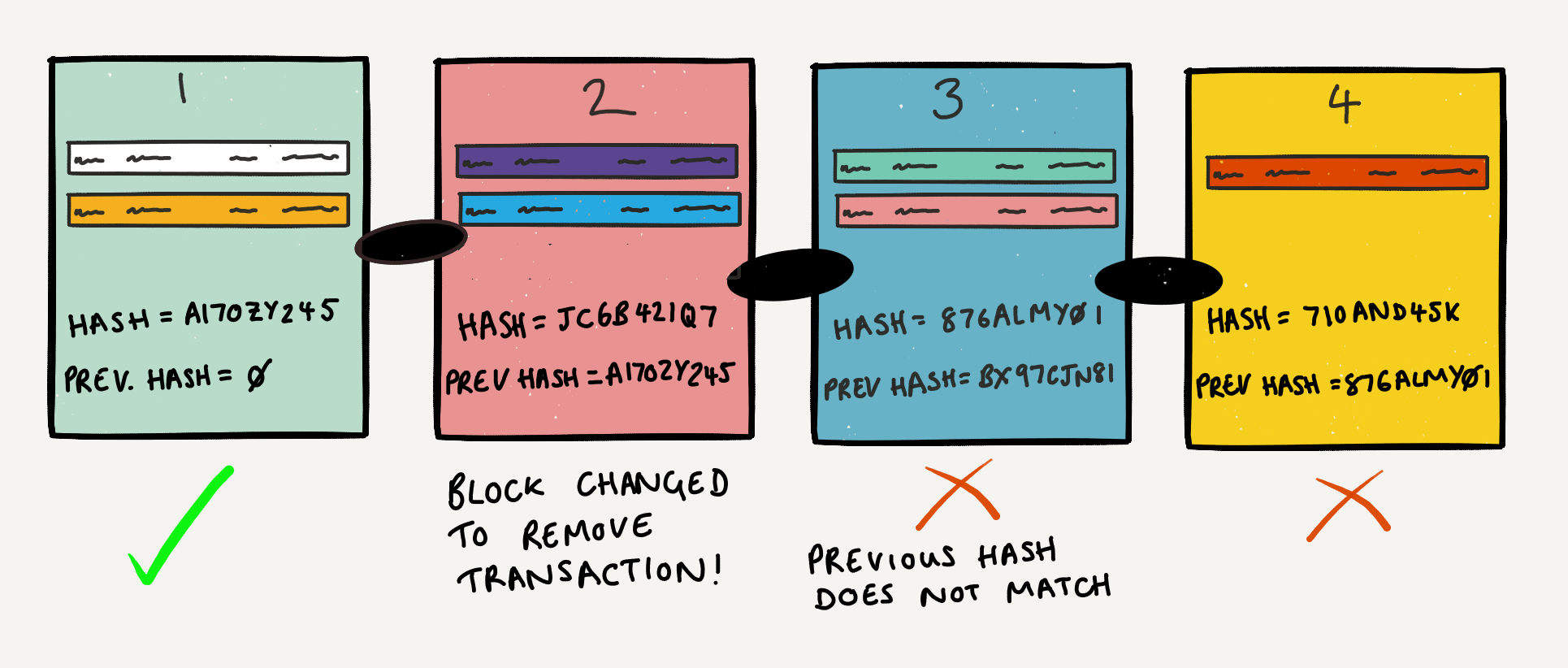
When the blocks validation process ends, they are permanently registered in the Blockchain and it is not possible to modify them without modifying at least all of the following blocks. Any attempt to modify a transaction would require great computing power, and still need to be validated by the other nodes.
In the final blockchain record, each block has an alphanumeric value called “hash”, which links it to the previous block. The hash contains data about the transactions and a date-time stamp. These features make it possible to track assets all the way back to the original one.
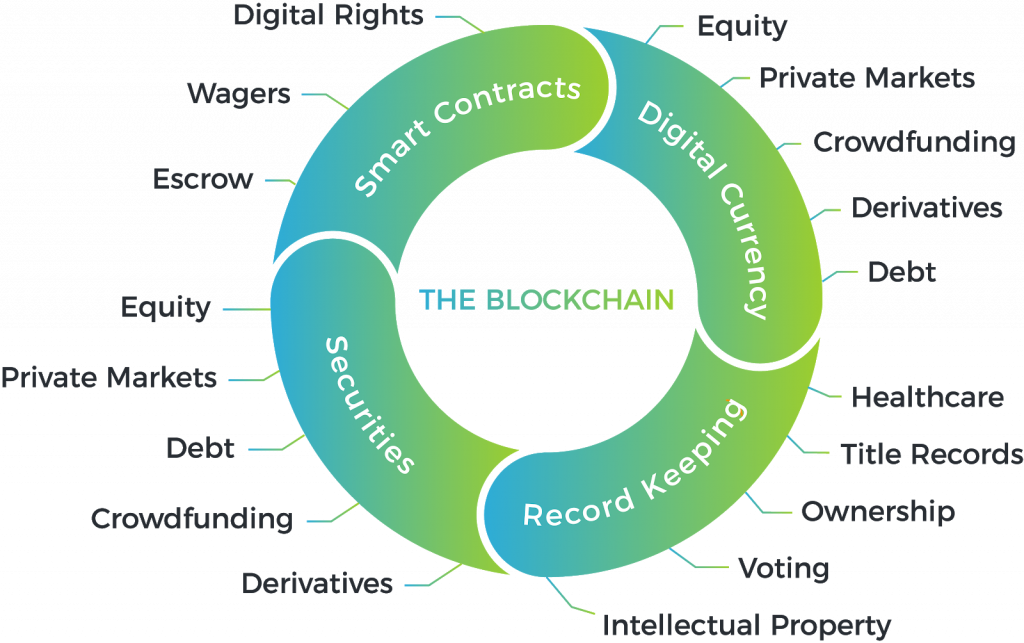
Blockchain outside finances
Blockchain, although it is closely related to the financial world due to its origin, is not exclusive to it. It has the potential to revolutionize markets, business, agriculture, livestock, legal systems, and even governments, It’s all about using imagination for making creative applications. Let’s see some examples:
Government: Using Blockchain in this area is very interesting, it could give absolute transparency. There are multiple areas of activity, from licensing management and public spending to identity management and social security. Related to the last one, people in the US are proposing the use of Blockchain to replace the social security numbers after the massive data theft in Equifax.
Music: The music industry could use the benefits of Blockchain. Spotify itself is betting strongly in this area with the recent purchase of Mediachain Labs, having the intention of improving the way they identify the rights owners of the songs. That would allow song distribution, copyright transfers, and payments to artists to become much more efficient.
Property Management: The Japanese government, is planning to consolidate all land and property records in a public book using Blockchain technology. This would let them have that information up to date, transparent, and secure.
Conclusion
We can summarize Blockchain works as a record that is shared by several or even millions of computers where transactions are archived. It uses an efficient process that is verifiable and permanent, yet without the need for intermediaries.
At this point, we understand why Blockchain is for everyone. It has a simple but ingenious way of sending information accurately from one point to another. The method is automated and yet, very safe. It has a built-in mechanism protecting the data, whereby trying to modify any single record would mean attempting to adjust the entire blockchain in millions of nodes.

